
MediCLI User Guide
Welcome to MediCLI!
Welcome to MediCLI - the solution to all your hospital management needs!
MediCLI is a desktop-based application that streamlines the management of patients, doctors, and appointments within a hospital. By combining the efficiency of a Command Line Interface (CLI) with an intuitive and comprehensive visual display, MediCLI presents itself as a robust solution for hospital clerks and administrators such as yourself. This guide will equip you with all the knowledge to become a MediCLI power user and truly transform your hospital management experience.
Who can benefit from MediCLI?
MediCLI is tailored built for hospital clerks/administrators or anyone who manages the relevant stakeholders in a hospital setting and seeks to optimize their workflow.
Prior knowledge:
MediCLI will be particularly beneficial for you are either (or both of):
- a fast-typer or,
- and familiar with a CLI, enabling you to get up to speed and perform tasks swiftly and efficiently.
That being said, even if you do not meet the above criteria, do not fret! Follow this guide, practice a little, and in only a couple of days you too can take full advantage of MediCLI’s features to manage doctors, patients, and appointments seamlessly.
Table of Contents
- Welcome to MediCLI!
- Who can benefit from MediCLI?
- Table of Contents
- Purpose of UG
- How to use this UG
- Key Product Information
- Quick Start Guide
- Features
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Known Issues
- Glossary
- Command summary
Purpose of UG
This User Guide (UG) guide provides step-by-step instructions, explanations, and tips to help users make the most out of MediCLI regardless of experience.
For new users
This UG offers a comprehensive overview of the features on offer, and provides you with a step-by-step guide on how to get started.
For experienced MediCLI users:
You may skip to the features section which elaborates on the individual commands that you can run to get the most out of the system.
How to use this UG
As you read through this MediCLI User Guide, you will come across a variety of different types of text formats. The table below will explain to you what they mean.
| Text Format | What it means |
|---|---|
| hyperlink | Text in blue are hyperlinks and will take you to a different page. |
command |
Text in lowercase with a grey background box are MediCLI commands. |
FIELD |
Text in uppercase with a grey background box are inputs to MediCLI commands |
[OPTIONAL_FIELD] |
Text in uppercase with a grey background box and square brackets are optional inputs to MediCLI commands |
Take note of these text-boxes, as they give you important information for using MediCLI.
Key Product Information
Product Description
MediCLI is a Java-based desktop application that allows you to manage your hospital with ease. Let’s now explore the product in more detail.
Overview of main features
Entities that you can manage with MediCLI
MediCLI allows you to manage three types of entities that are common in a hospital setting:
- Doctors: The doctors employed by your hospital
- Patients: The patients that are treated at your hospital
- Appointments: A medical appointment between a doctor and a patient that takes place at a specified time
Operations that you can perform with MediCLI
MediCLI allows you to perform the following operations of each of the entities above:
- Add: Add entities to the application
- Delete: Delete entities from the application
- Query: Lookup an entity in the application based on some criteria
- Edit: Edit the attributes of entities
Other notable features
On top of the primary entities and operations highlighted above, MediCLI also provides the following capabilities:
- Persistent storage of information across restarts of the application
- A clean and minimalist display to view relevant information on entities
- Thorough error messages and in-app prompts guide you on how to overcome any issues you may run into.
Quick Start Guide
Ready to step into the world of MediCLI? This section will provide detailed information on how users can get started, which includes basic system requirements, installation instructions, an overview of the main window, and a tutorial on using the command-line interface (CLI).
System Compatibility
MediCLI is written with the Java programming language on the backend and JavaFX on the front end. Therefore, a device with Java version 11 or above and JavaFX version 17 or above installed is required to run MediCLI.
Compatible Operating Systems:
- Any device running Windows, macOS, or Ubuntu with sufficient Java and JavaFX compatibility.
Recommended Minimum System Requirements:
- 2-core CPU running at 2.40 GHz
- 4GB RAM
- 2GB free disc space
Installation Instructions
-
Please make sure the computer you are using meets the system compatibility specified above.
-
Download the latest
MediCLI.jarfrom here.
-
We recommend you copy the file into the folder you want to use as the home folder for MediCLI. This is because running the application will create additional storage and logging files.
-
Congratulations! You now have MediCLI successfully downloaded on your computer.
Starting up MediCLI
Once you have installed MediCLI onto your computer (refer to the sub-section above), navigate to the instructions specific to your operating system below.
Windows
-
Open File Explorer and navigate to the home folder containing the MediCLI jar file.
-
Double-click on the MediCLI application and it should start up!
macOS
-
Open Finder and navigate to the home folder containing the MediCLI jar file.
-
Double-click on the MediCLI application and it should start up!
CLI Alternative Solution
-
Open a command terminal,
cdinto the home folder containing the MediCLI jar file, and use thejava -jar MediCLI.jarcommand to run the application.
A GUI similar to the one below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.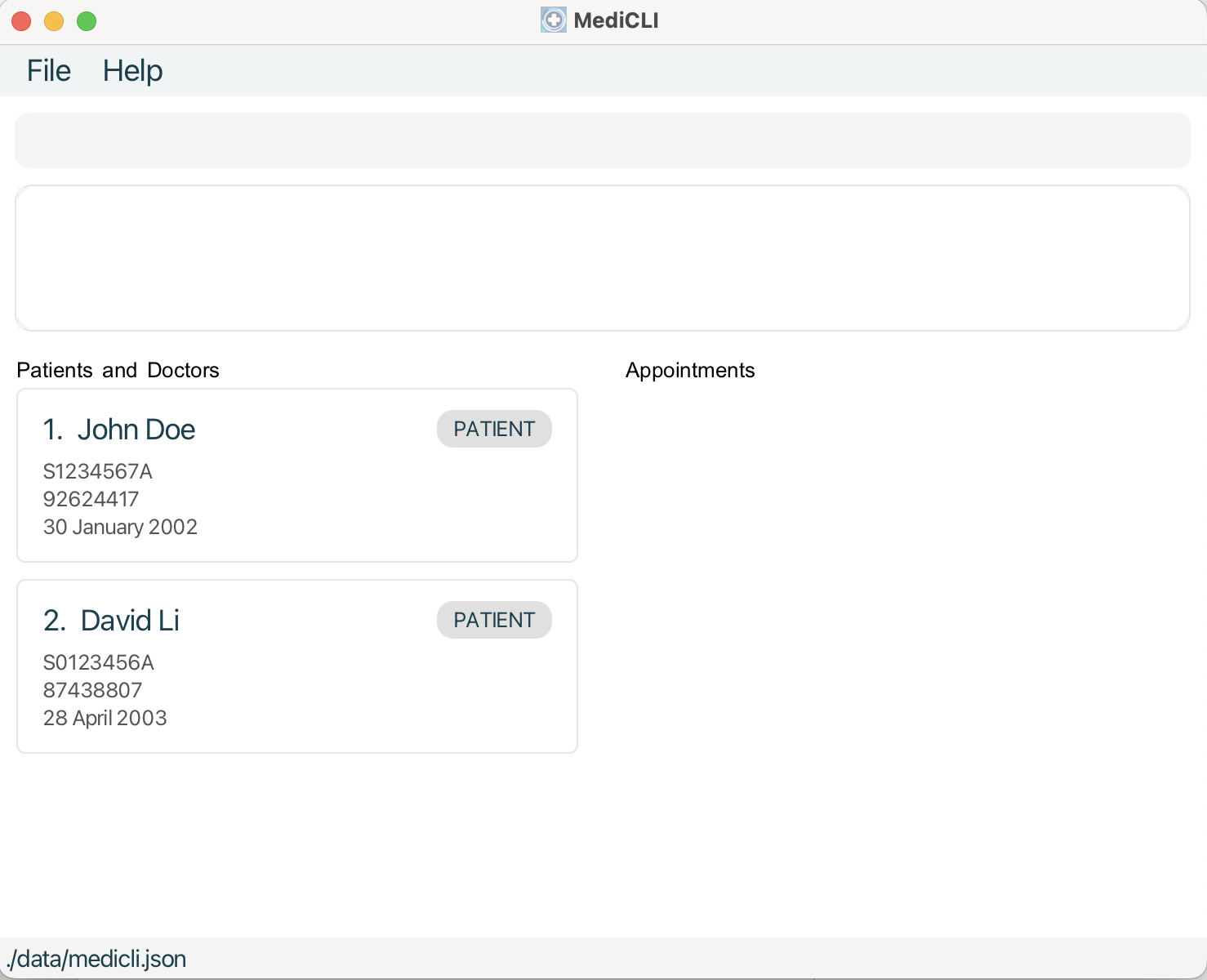
Overview of MediCLI Main Window
MediCLI has 4 primary components in its main window. Detailed descriptions of each can be found below.
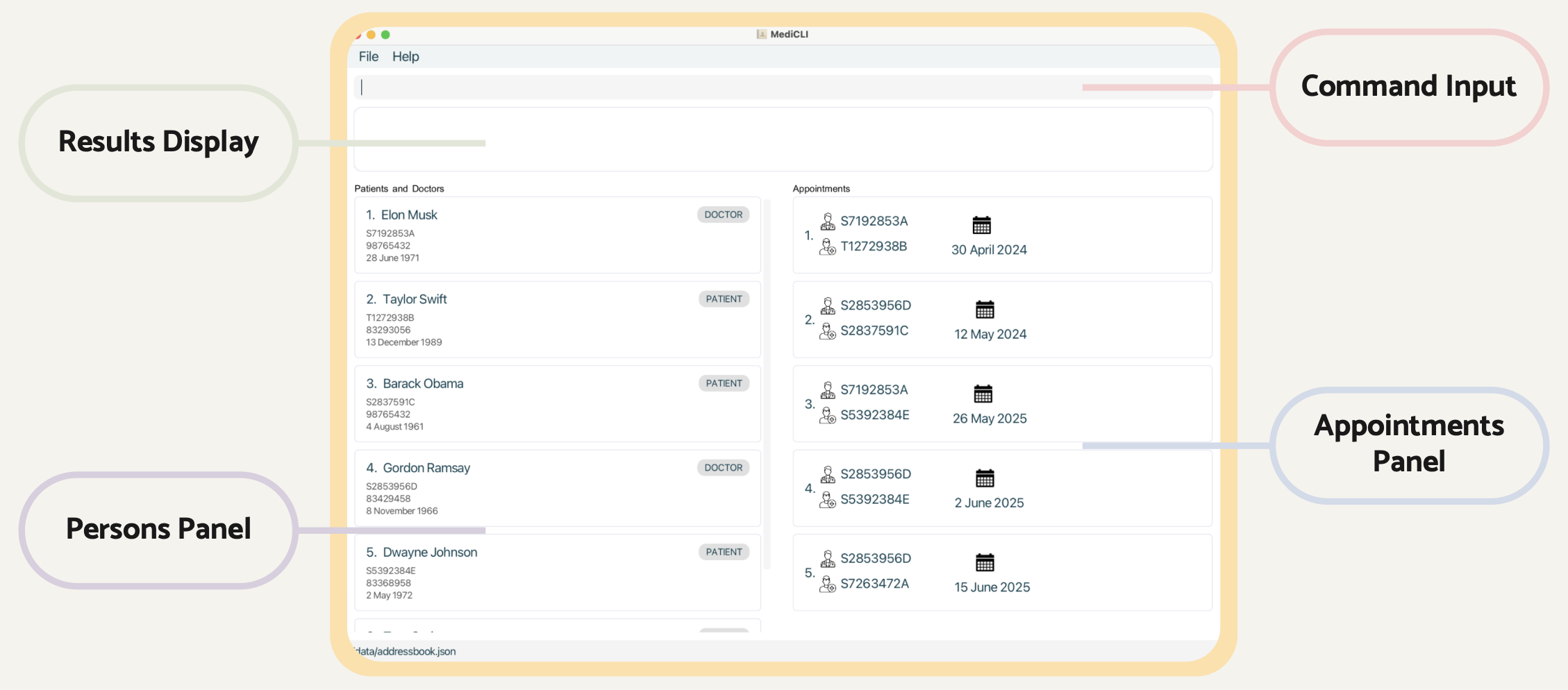
Command Input - This is where you will type your commands.
Results Display - MediCLI will respond to you here with either a success message or a detailed description of what went wrong.
Persons Panel - This is where you will see a list of the filtered patients and patients.
Appointments Panel - This is where you will see a list of the filtered patients and patients.
How to use the command line interface (CLI)
MediCLI is operated using typed commands to the command line interface (CLI). Do not worry if you do not understand CLI yet; here we will explain to you the formats of text commands and how to use them.
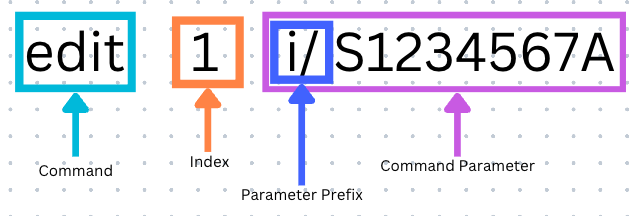
| CLI Format | What it means |
|---|---|
| Command | The command tells MediCLI what action you want to perform. |
| Index | Certain MediCLI commands have an INDEX field, which is a number that is assigned to a particular patient, doctor, or appointment. Index must be larger than 1 and can be up to the maximum number of patients/doctors or appointments as listed in the MediCLI GUI. |
| Parameter Prefix | Fields typically have a prefix like i/ or n/ followed by the field content. This tells MediCLI what field you are entering. |
| Command Parameter | The command parameter is the parameter prefix followed by field content. For example, the command parameter to enter NRIC would be i/S1234567A
|
clear.Quick Tutorial on a Sample Use Case
- Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try (Assuming MediCLI is opened for the first time and is in its initial state with the default sample data):
-
list: Lists all contacts. -
adddoctor i/S1234567B n/Amy Smith d/2003-01-30 p/98765432: Adds a doctor namedAmy Smithto the MediCLI system. -
addappt ad/2024-06-09 10:15 dn/S1234567B pn/S1234567A: Schedules an appointment between the doctorAmy Smithand the patientJohn Doe.
-
delete 2: Deletes the 2nd person currently listed in the MediCLI system (patient named David Li). -
exit: Exits the app.
- Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Features
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by you.
e.g. inaddpatient i/NRIC n/NAME d/DOB p/PHONE,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asn/John Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.g.edit INDEX [i/NRIC] [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [d/DOB]can be used asedit 1 n/John Doeor asedit 1 i/t1234567s. -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE,p/PHONE n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,list,exitandclear) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp.
Person Related Commands
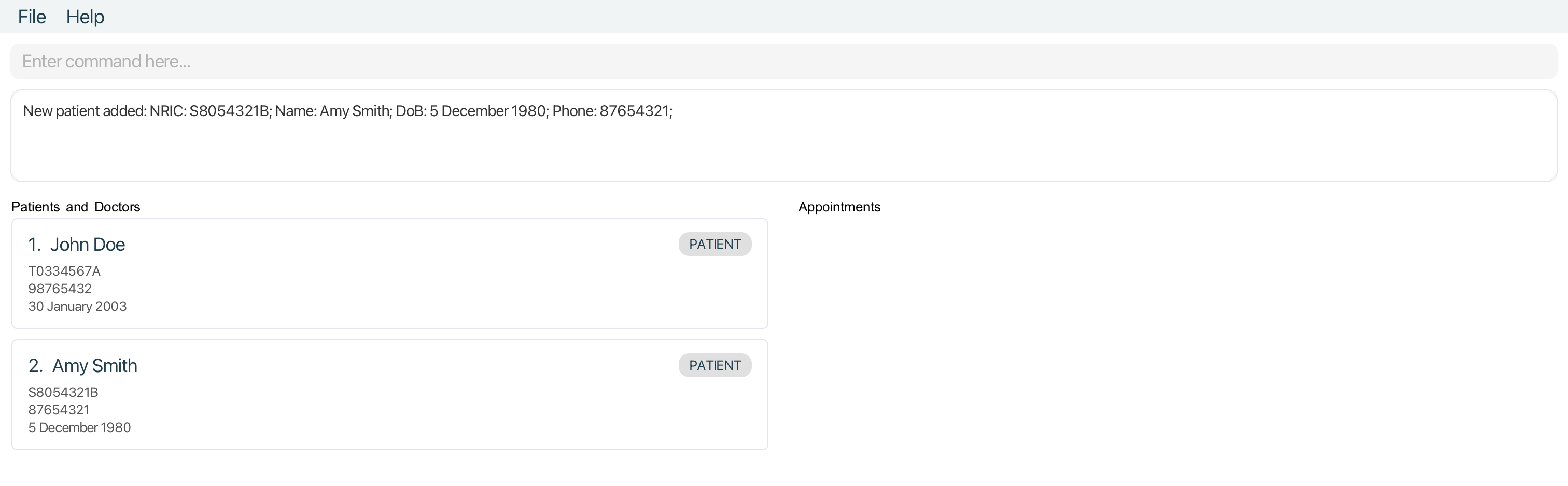
Adding a patient : addpatient
Adds a patient into the MediCLI system.
Format: addpatient i/NRIC n/NAME d/DOB p/PHONE
Field Constraints:
- NRIC : Follows the correct Singapore NRIC format. Begin with one of S, T, G, F, or M, followed by 7 numerical digits, then end with an alphabetical letter. This field is non-case-sensitive.
- NAME : Only contain alphabetical characters and spaces. This field is non-case-sensitive.
- DOB : Only contain numerical characters in the format yyyy-MM-dd. Acceptable date range is from 1900 January 1st to today’s date.
- PHONE : Only contain numerical characters and of exactly 8 digits long.
Command Constraints:
- All of the above fields (NRIC, NAME, DOB, and PHONE) are compulsory and must be non-empty.
- Command fails if there already exists a person (patient or doctor) in the MediCLI system that has the same NRIC as the one given.
- The ordering of the fields does not influence the command.
Examples:
addpatient i/T0334567A n/John Doe d/2003-01-30 p/98765432addpatient n/Amy Smith i/S8054321B p/87654321 d/1980-12-05
Adding a doctor : adddoctor
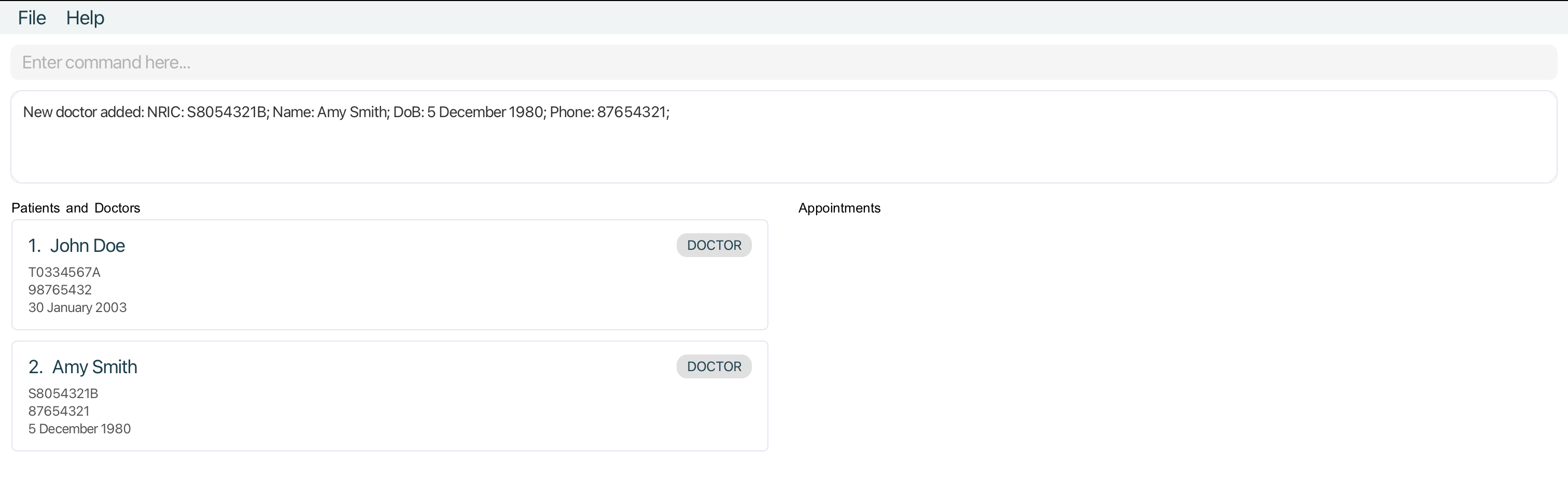
Adds a doctor into the MediCLI system.
Format: adddoctor i/NRIC n/NAME d/DOB p/PHONE
Field Constraints:
- NRIC : Follows the correct Singapore NRIC format. Begin with one of S, T, G, F, or M, followed by 7 numerical digits, then end with an alphabetical letter. This field is non-case-sensitive.
- NAME : Only contain alphabetical characters and spaces. This field is non-case-sensitive.
- DOB : Only contain numerical characters in the format yyyy-MM-dd. Acceptable date range is from 1900 January 1st to today’s date.
- PHONE : Only contain numerical characters and of exactly 8 digits long.
Command Constraints:
- All of the above fields (NRIC, NAME, DOB, and PHONE) are compulsory and must be non-empty.
- Command fails if there already exists a person (patient or doctor) in the MediCLI system that has the same NRIC as the one given.
- The ordering of the fields does not influence the command.
Examples:
adddoctor i/T0334567A n/John Doe d/2003-01-30 p/98765432adddoctor n/Amy Smith i/S8054321B p/87654321 d/1980-12-05
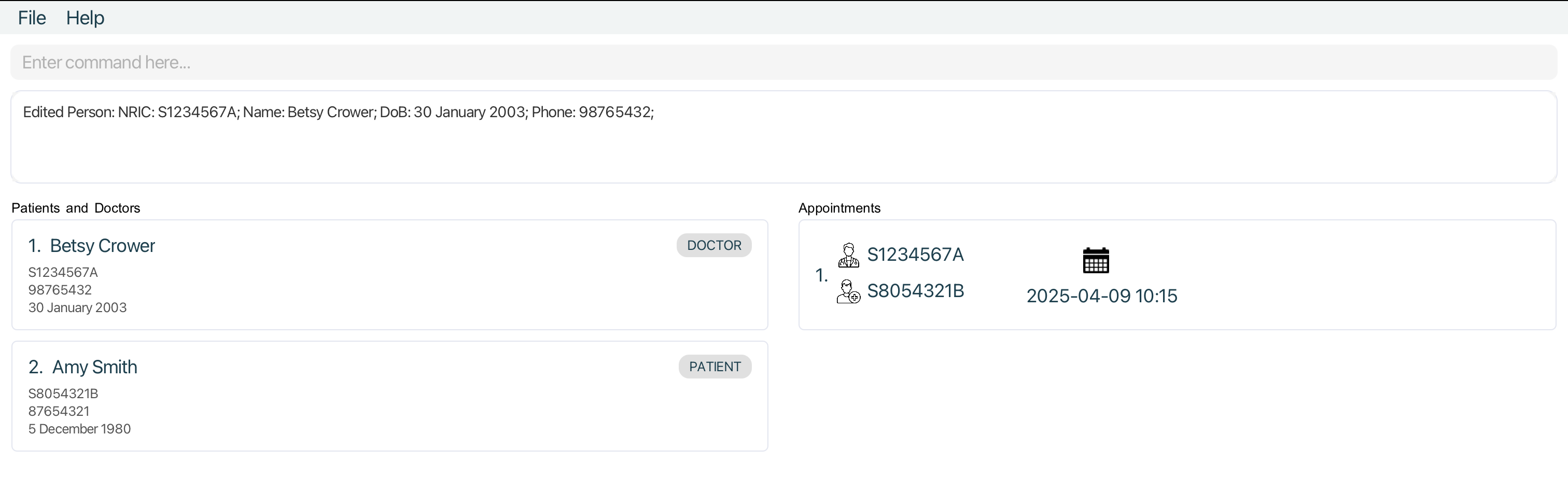
Editing a person : edit
Edits an existing person in the MediCLI system. Edits the patient or doctor at the specified INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list.
Existing values will be updated to the input values.
Format: edit INDEX [i/NRIC] [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [d/DOB]
Field Constraints:
- NRIC : Follows the correct Singapore NRIC format. Begin with one of S, T, G, F, or M, followed by 7 numerical digits, then end with an alphabetical letter. This field is non-case-sensitive.
- NAME : Only contain alphabetical characters and spaces. This field is non-case-sensitive.
- DOB : Only contain numerical characters in the format yyyy-MM-dd. Acceptable date range is from 1900 January 1st to today’s date.
- PHONE : Only contain numerical characters and of exactly 8 digits long.
Command Constraints:
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
- At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Command fails if there already exists a person (patient or doctor) in the MediCLI system that has the same NRIC as the one given.
- The ordering of the fields does not influence the command.
Examples:
-
edit 1 i/S1234567A n/Betsy CrowerEdits the NRIC and name of the 1st person to bes1234567aandBetsy Crowerrespectively.
Finding both doctor and patient by name : find
Find Patient(s) or Doctor(s) whose details contain any of the given keywords.
Format for querying patients or doctors: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Command Constraints:
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
hanswill matchHans - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - Only the name field is searched.
- Both full words and substrings will be matched e.g.
Hanwill matchHans - Patients and Doctors matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e. logical ‘OR’ search).
e.g.
Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang
Examples:
-
find JohnreturnsjohnandJohn Doe -
find John Davidreturns patientJohn Doe, doctorDavid Li
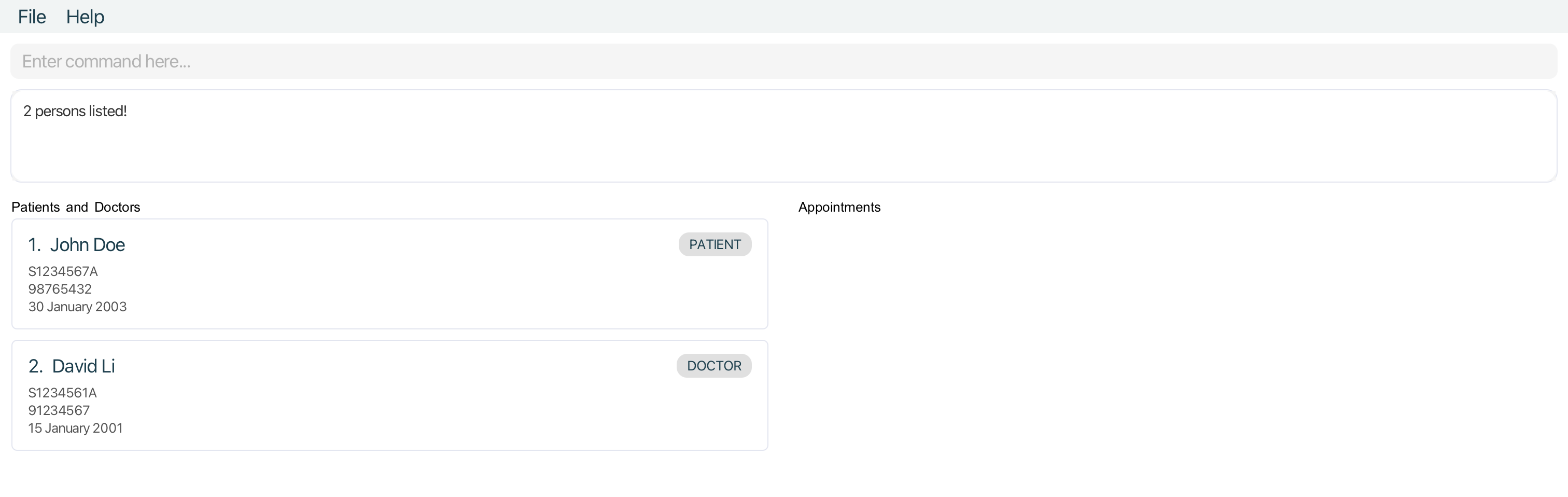
find command to filter people for commands that require a person’s INDEX.Querying patients by name : patient
Find Patient(s) whose details contain any of the given keywords.
Format for querying Patients: patient KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Command Constraints:
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
hanswill matchHans - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - All person fields are searched and matched (Name, NRIC, Phone Number, DoB).
- Both full words and substrings will be matched e.g.
Hanwill matchHans - Patients matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang
Examples:
-
patient John Davidreturnspatientwith nameJohn Doeandpatientwith nameDavid Li -
patient S1234returnspatientwithNricS1234567A,patientwithNricS1234765Q -
patient 30 JanreturnspatientwithDoB30 January 1990,patientwithDoB30 January 2001
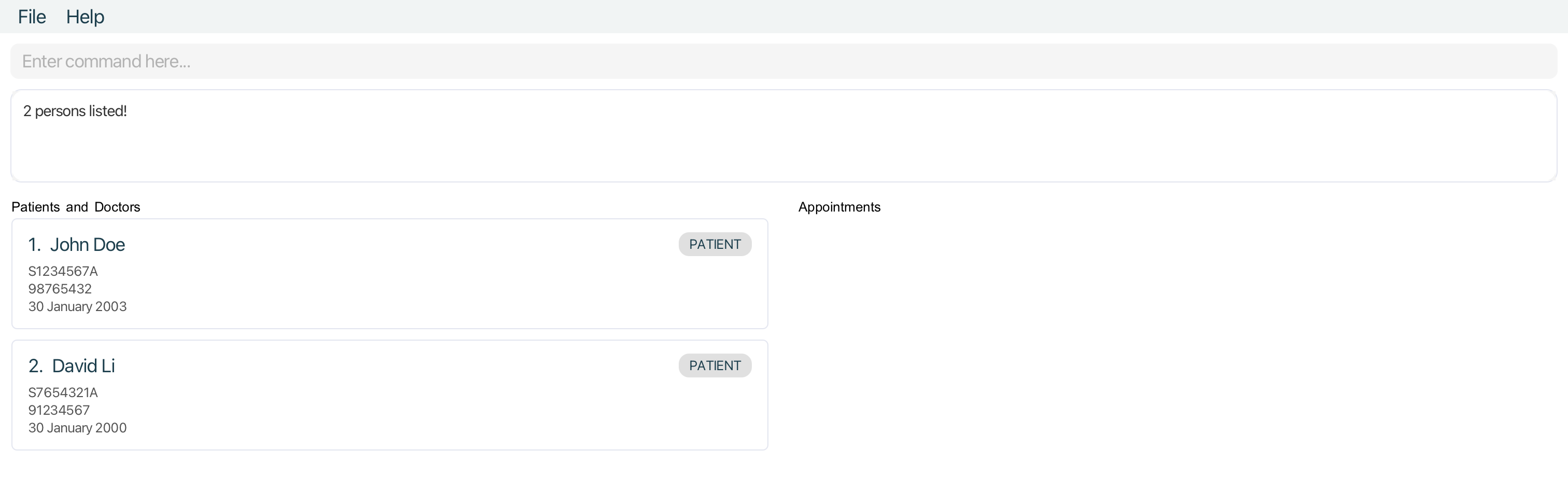
Querying doctors by name : doctor
Find Doctors(s) whose details contain any of the given keywords.
Format for querying Doctors: doctor KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Command Constraints:
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
hanswill matchHans - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - All person fields are searched and matched (Name, NRIC, Phone Number, DoB).
- Both full words and substrings will be matched e.g.
Hanwill matchHans - Doctors matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e. logical ‘or’ search).
e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang
Examples:
-
doctor John Davidreturnsdoctorwith nameJohn Doeanddoctorwith nameDavid Li -
doctor S1234returnsdoctorwithNricS1234567A,doctorwithNricS1234765Q -
doctor 30 JanreturnsdoctorwithDoB30 January 1990,doctorwithDoB30 January 2001
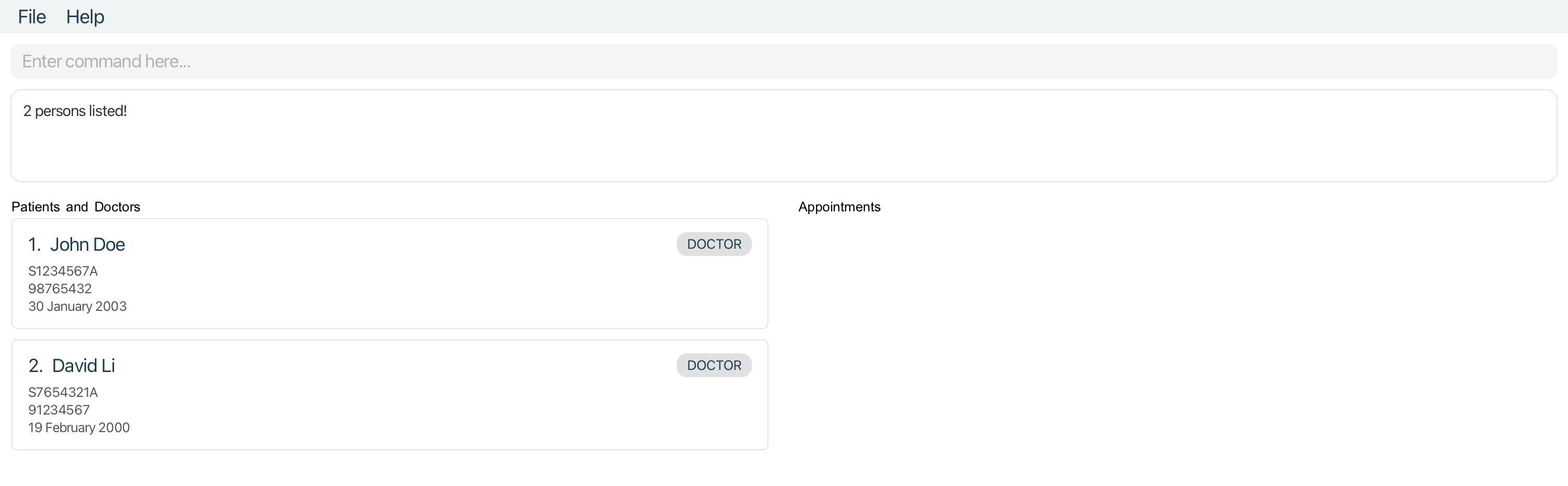
Deleting a doctor or patient : delete
Deletes the specified doctor / patient from the MediCLI system. Note that all associated appointments with this doctor / patient will also be recursively deleted. Please exercise caution when using the delete command and removing a patient or a doctor from MediCLI, as this action cannot be undone.
- Deletes the doctor / patient at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed doctor and patient list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
listfollowed bydelete 2deletes the 2nd doctor / patient in the MediCLI system. -
patient Johnfollowed bydelete 1deletes the 1st patient in the results of thepatientsearch command. -
doctor Stevefollowed bydelete 2deletes the 2nd doctor in the results of thedoctorsearch command.
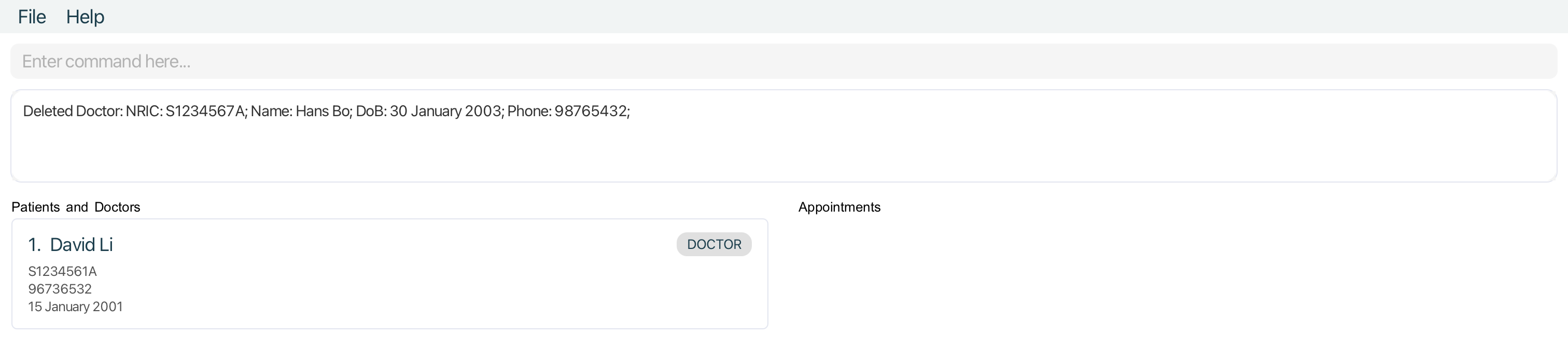
Appointment Related Commands
Adding an appointment : addappt
Adds an appointment to MediCLI. Appointments are between a doctor with the specified DOCTOR_NRIC and a patient with the PATIENT_NRIC on a specific date and time.
Format: addappt ad/DATETIME dn/DOCTOR_NRIC pn/PATIENT_NRIC
patient and doctor commands to retrieve their NRIC number if you only remember their name.Field Constraints:
-
DATETIME: Input must be in the format
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm. Specified date and time must be later than the current date and time. i.e. appointment cannot be scheduled in the past. - DOCTOR_NRIC: Follows the correct Singapore NRIC format. Begin with one of S, T, G, F, or M, followed by 7 numerical digits, then end with an alphabetical letter. This field is non-case-sensitive.
- PATIENT_NRIC: Follows the correct Singapore NRIC format. Begin with one of S, T, G, F, or M, followed by 7 numerical digits, then end with an alphabetical letter. This field is non-case-sensitive.
Command Constraints:
- All of the above fields (
DATETIME,DOCTOR_NRIC,PATIENT_NRIC) are compulsory and must be non-empty. - A doctor with the specified
DOCTOR_NRICmust already exist in the MediCLI System. - A patient with the specified
PATIENT_NRICmust already exist in the MediCLI System.
Examples:
addappt ad/2024-08-11 23:50 dn/S1234567A pn/S1234567Baddappt ad/2025-04-09 11:10 dn/S8054321B pn/T0334567A
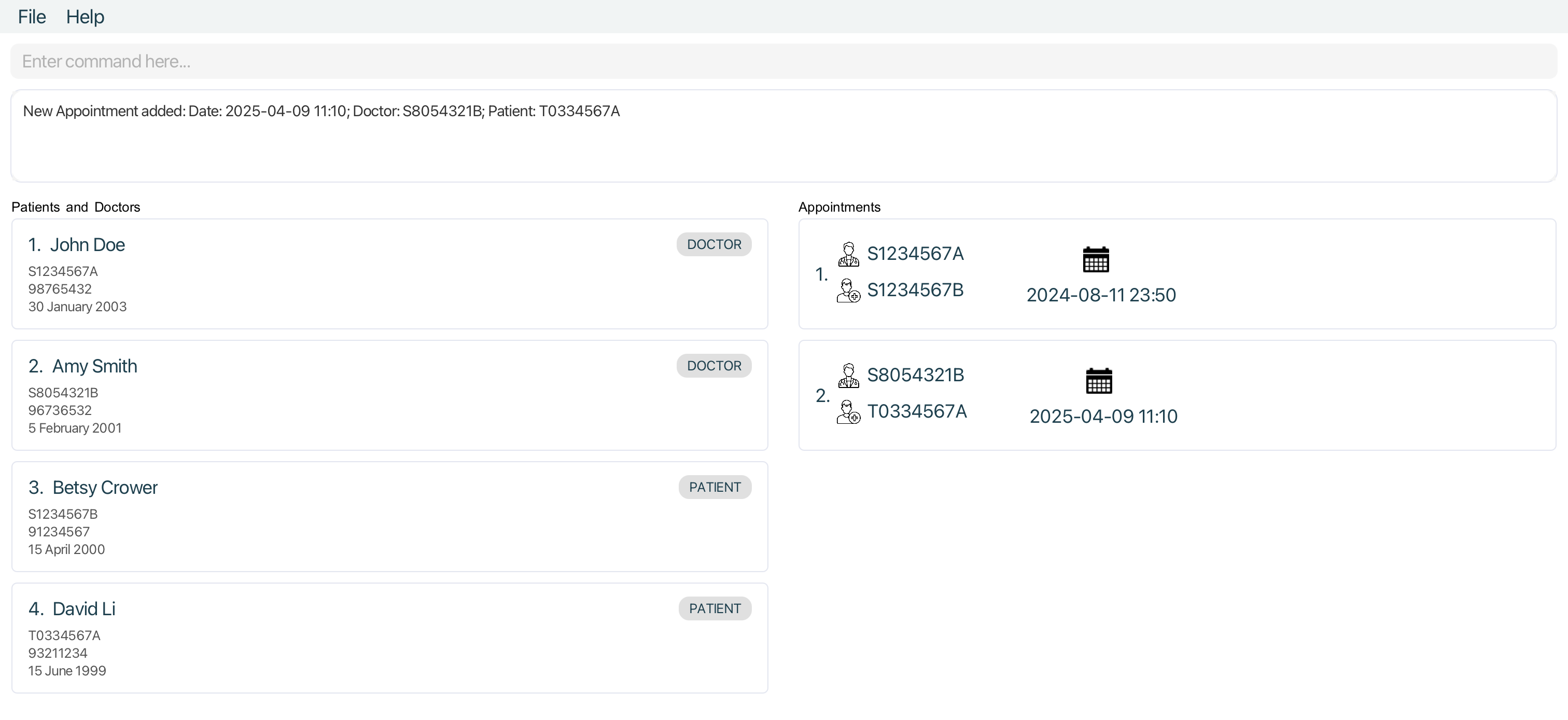
Editing an appointment : editappt
Edits an existing appointment in the MediCLI system. Edits the appointment at the specified INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed appointments list.
Existing values will be updated to the input values.
Format: editappt INDEX ad/DATETIME
- Edits the appointment at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed appointment list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - Existing values will be updated to the input values.
Field Constraints:
-
DATETIME : Input must be in the format
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm. Specified date and time must be later than the current date and time. i.e. appointment cannot be scheduled in the past.
Command Constraints:
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
- At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
Examples:
-
editappt 1 ad/2025-04-09 11:00Edits the appointment date and time of the first appointment in the appointment list to2025-04-09 11:00
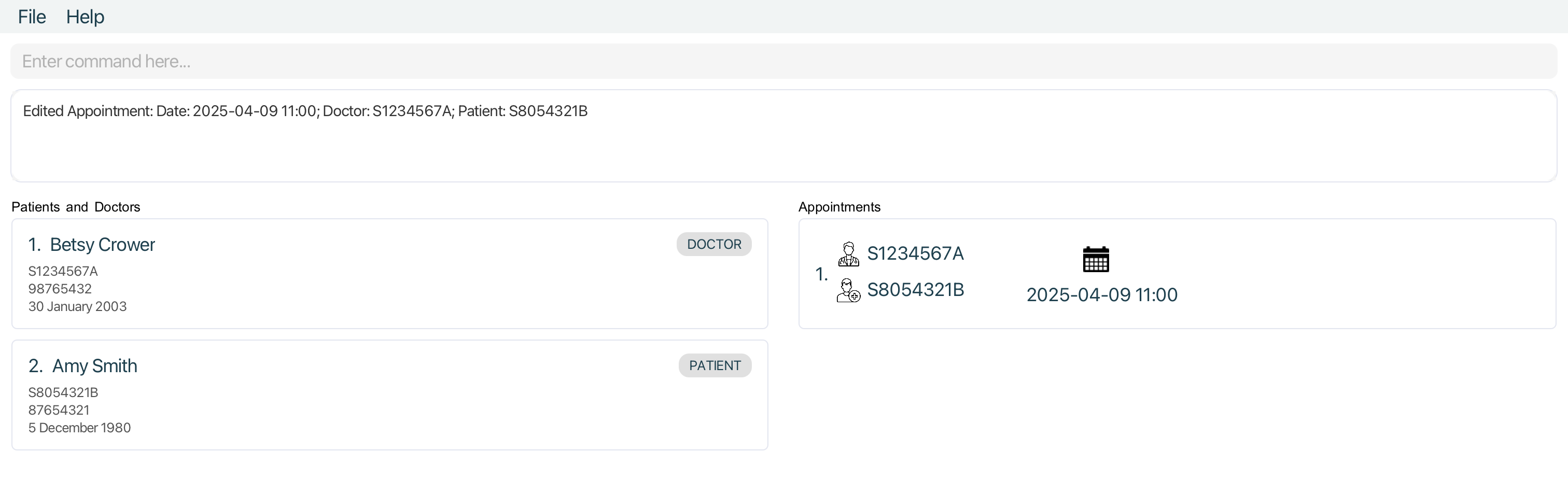
Querying appointments by patient’s NRIC : apptforpatient
Format: apptforpatient KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Command Constraints:
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
s1234562awill matchS1234562A - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
S1234562A S1234561Awill
match appointments that involveS1234562AandS1234561A. - Only the NRIC field of
Patientis searched and matched. - Only exact NRICs will be matched e.g.
S123456will not matchS1234562A - Appointments with
Patients whose NRICs match at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.ORsearch).
Example:
-
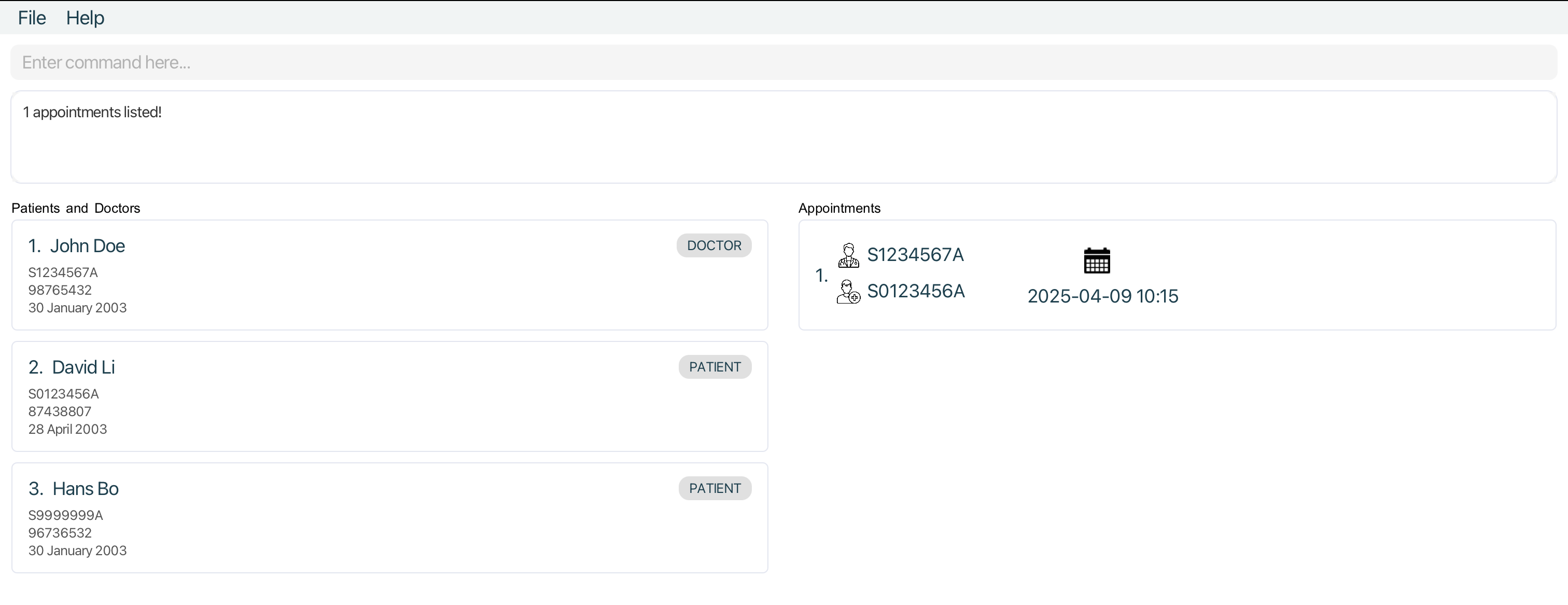
apptforpatient s0123456areturns allAppointmententries thatPatientwithNricS0123456Ais involved in. -
All
Appointments listed
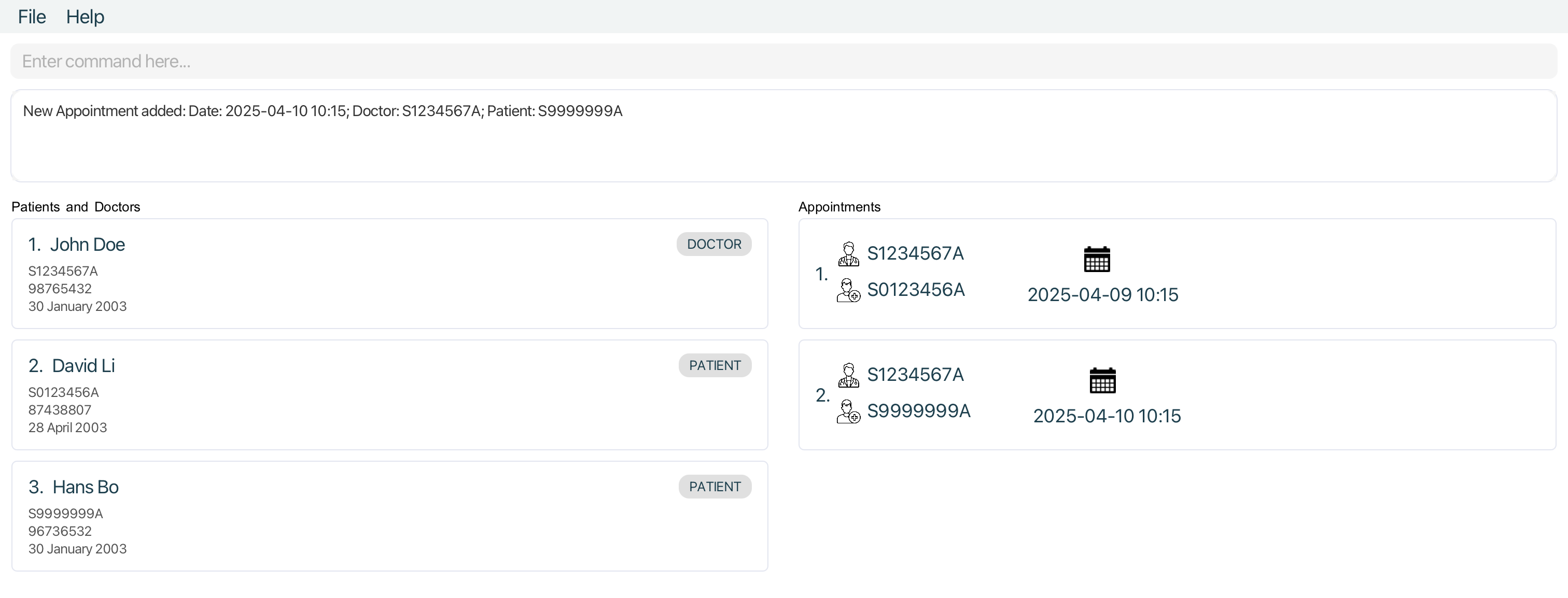
-
Only
Appointments withPatientofNricS0123456A
Querying appointments by doctor’s NRIC : apptfordoctor
Format: apptfordoctor KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Command Constraints:
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
s1234562awill matchS1234562A - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
S1234562A S1234561Awill
match appointments that involveS1234562AandS1234561A.- Only the NRIC field of
Doctoris searched and matched.
- Only the NRIC field of
- Only exact NRICs will be matched e.g.
S123456will not matchS1234562A - Appointments with
Doctors whose NRICs match at least one keyword will be returned (e.g.ORsearch).
Example:
-
apptfordoctor s1234561areturns allAppointmentobject(s) thatDoctorwith NRICS1234561Ais involved in. -
All
Appointments listed
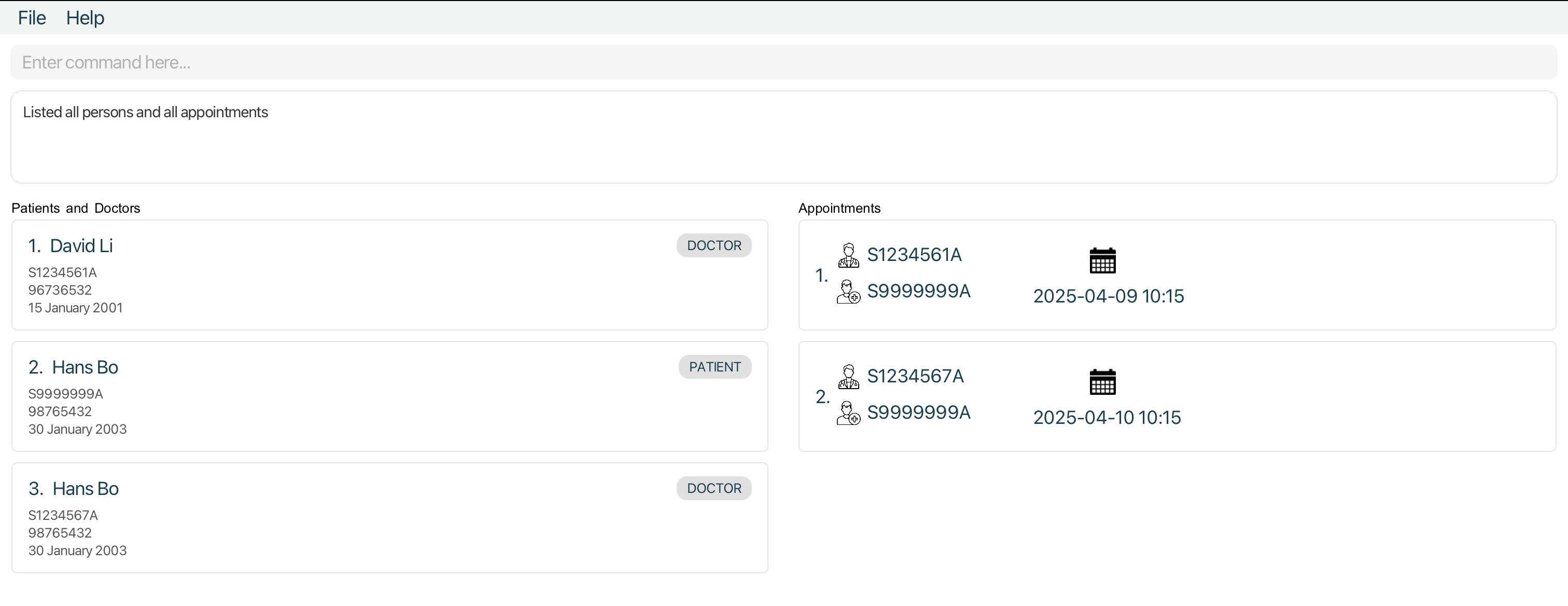
-
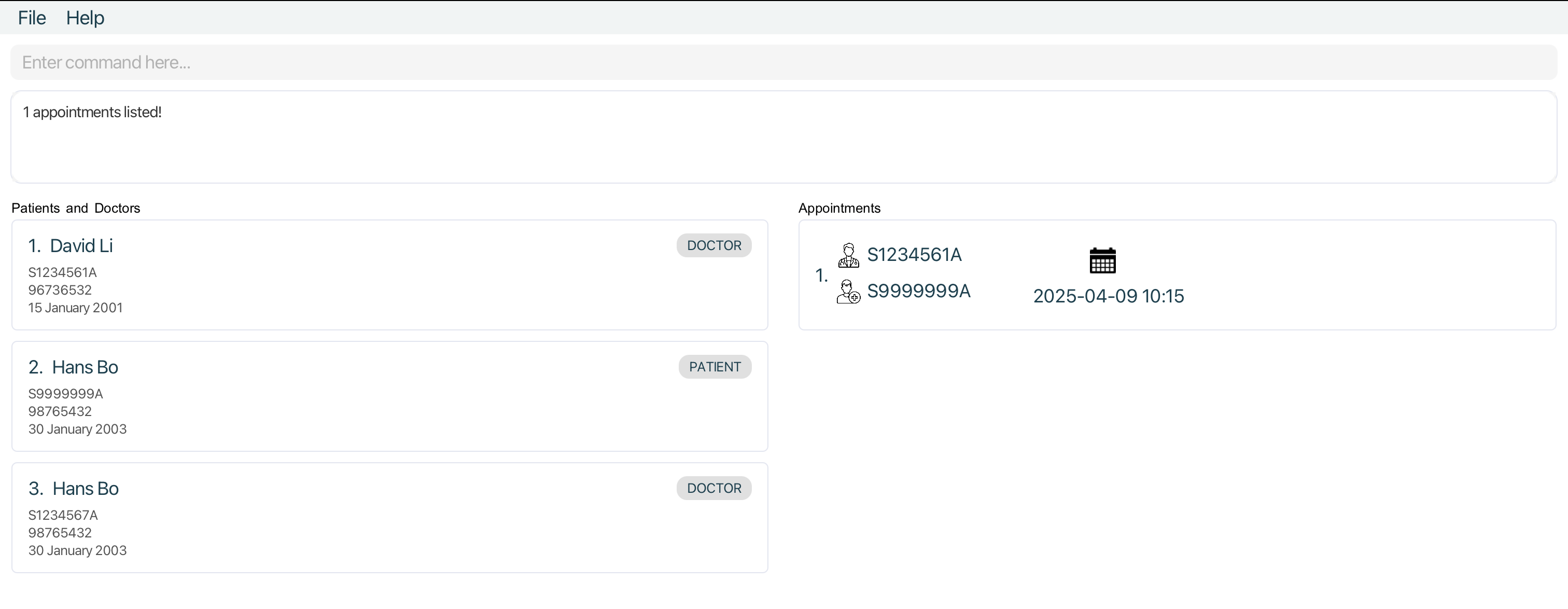
Only
Appointments withDoctorofNricS1234561A
Deleting appointment : deleteappt
Deletes the specified appointment from the MediCLI system.
Format: deleteappt INDEX
- Deletes the appointment at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed appointments list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
listfollowed bydeleteappt 2deletes the 2nd appointment in the MediCLI system. -
apptforpatient S1234567Afollowed bydeleteappt 1deletes the 1st appointment in the results of theapptforpatientsearch command. -
apptfordoctor S1234567Bfollowed bydeleteappt 2deletes the 2nd appointment in the results of theapptfordoctorsearch command.
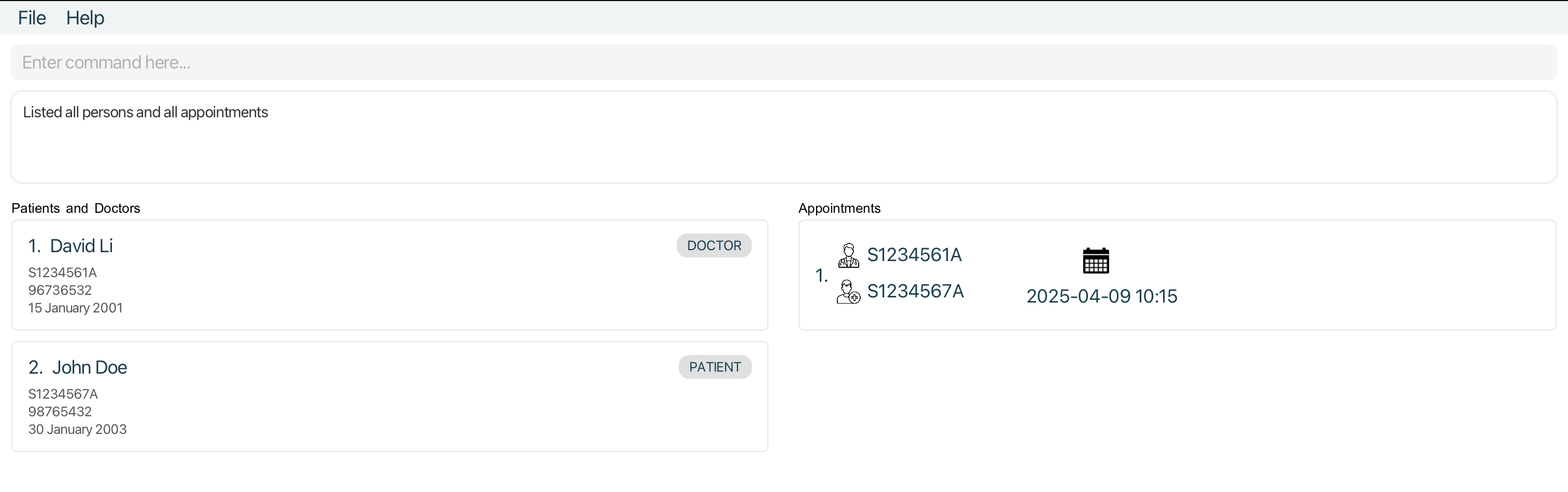
Visual Guide
- All appointments listed after running
list
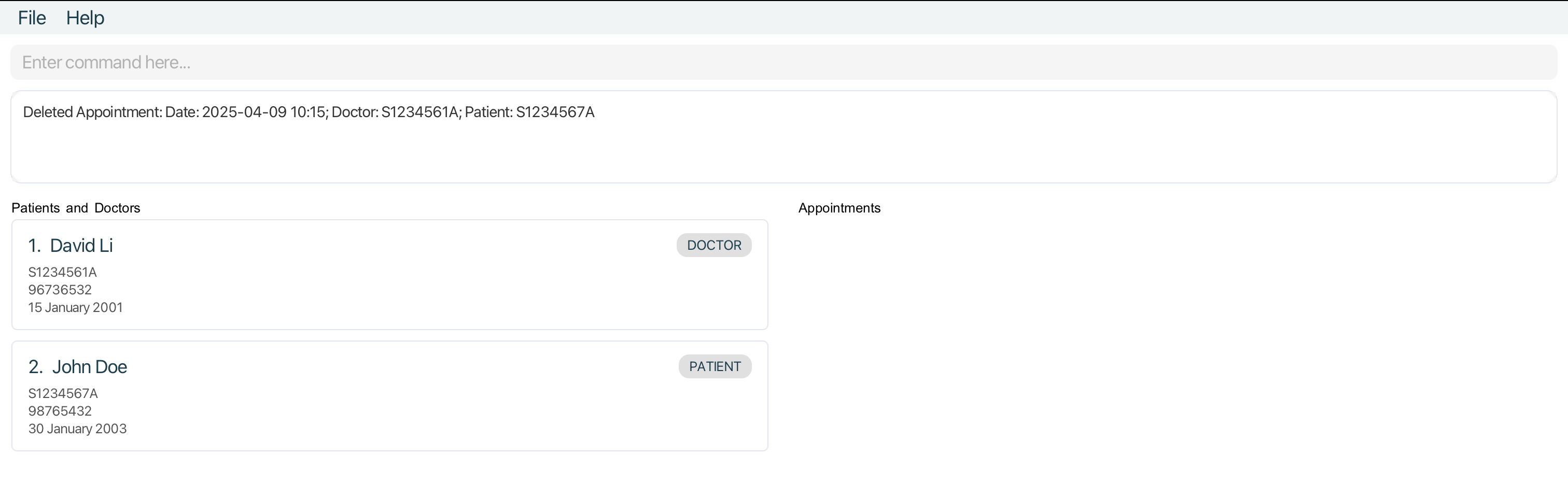
- After running
deleteapptwithIndexof1
Miscellaneous Commands
Viewing help : help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page.

Format: help
Listing all persons : list
Shows a list of all persons (patients & doctors) and appointments in the MediCLI system.
Format: list
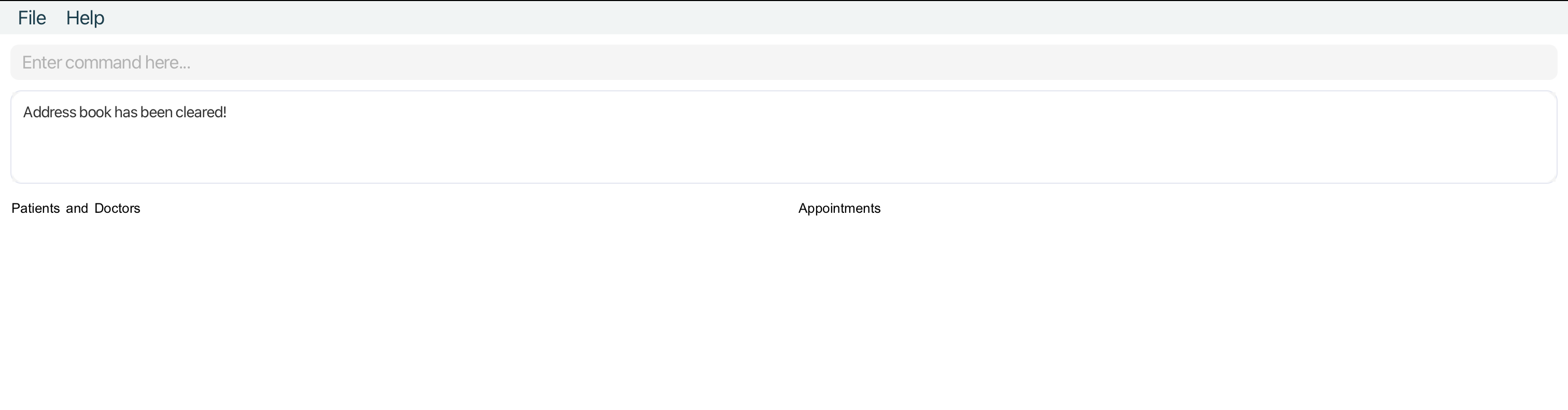
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from MediCLI.
Format: clear
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
Saving the data
MediCLI data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
MediCLI data are saved automatically as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/MediCLI.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Furthermore, certain edits can cause the MediCLI to behave in unexpected ways (e.g. if a value entered is outside of the acceptable range). Therefore, edit the data file only if you are confident that you can update it correctly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app on the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous MediCLI home folder. -
Q: Can I use MediCLI on different operating systems?
A: Yes, MediCLI is compatible with multiple operating systems as long as you have Java 11 or above installed. You can run it on Windows, macOS, or Linux. -
Q: Is there a limit to the number of patients, doctors, or appointments I can add to MediCLI?
A: There is no built-in limit to the number of entries you can add to MediCLI. However, the performance may be affected if you add an extremely large number of entries. -
Q: Can I customise the appearance or theme of the interface in MediCLI?
A: Currently, there is no option to customise the appearance or theme of the interface in MediCLI. It has a default interface optimised for efficiency and usability. -
Q: Does MediCLI support multi-user access or user authentication?
A: No, MediCLI is designed for single-user access only. It does not have built-in support for multi-user access or user authentication. -
Q: Can I export data from MediCLI to other formats like CSV or Excel?
A: Currently, there is no built-in feature to export data from MediCLI to other formats. However, you can manually extract data from the JSON file if needed.
Known Issues
-
Issue: When using multiple screens, if the MediCLI application is moved to a secondary screen and later switched to using only the primary screen, the graphical user interface (GUI) may open off-screen upon application launch.
Impact: Users may find it challenging to interact with the application as the GUI is rendered off-screen, making it inaccessible and difficult to use.
Workaround: To resolve this issue, users can delete the preferences.json file generated by the application before launching MediCLI again. This action resets the application preferences, ensuring that the GUI opens within the visible area of the primary screen.
-
Issue: MediCLI may experience performance degradation when handling a large number of entries, such as patients, doctors, or appointments.
Impact: Users may notice slower response times or delays when adding, editing, or deleting entries, especially in cases with a large dataset.
Workaround: Users can optimise performance by limiting the number of entries stored in MediCLI or by periodically archiving old data to reduce the dataset size.
-
Issue: Editing data directly in the data file may lead to unexpected behavior or data corruption.
Impact: Users who manually edit the JSON data file used by MediCLI may inadvertently introduce errors or inconsistencies, resulting in data loss or application crashes.
Workaround: It’s recommended to avoid directly editing the data file unless absolutely necessary. Users should exercise caution and make backups before making any changes to the data file.
-
Issue: MediCLI does not provide built-in data export functionality to formats like CSV or Excel.
Impact: Users may face challenges when trying to export data from MediCLI for analysis or reporting purposes, especially if they rely on external tools or software that require specific file formats.
Workaround: Users can manually extract data from the JSON data file used by MediCLI and convert it to the desired format using third-party tools or scripts. Alternatively, they can explore custom export solutions or request this feature from the developers.
-
Issue: When the name entered into the system is too lengthy, MedicCLI truncates the name and adds ellipses.
Impact: Users may face challenges reading or finding long names when reading from MediCLI, especially on smaller displays.
Workaround: Users can reduce the amount of characters typed into the name field or search for longer names based on the first few characters shown instead of the entire name.
-
Issue: When the name entered into the system contains acute accents (e.g.
Aimée), Chinese characters, or dash-, the system will reject it.Impact: Users may face challenges entering information about patient / doctors with foreign names into MediCLI.
Workaround: Users can replace the accented characters with normal alphabets (e.g.
éwithe), omit the dash and romanize Chinese names. -
Issue: MediCLI will only accept Singaporean NRIC
Impact: Users may face challenges entering information about patients who are not from Singapore (e.g. those without NRIC).
Workaround: There is currently no workaround, but the MediCLI development team will add this feature enhancement in the near future.
-
Issue: MediCLI currently allows scheduling of appointments between the same doctor but different patients at identical times (e.g. overlapping appointments).
Impact: Users may schedule two or more patients with the same doctor at the same time when the doctor can only see one patient at any given time.
Workaround: Users can first look up the appointments of the doctor and visually confirm the doctor is free at a given time before scheduling a patient with them.
Glossary
Alphanumeric: A combination of alphabetic characters and numerical digits. (e.g S1234567A)
Backend: The part of a software system that handles data processing and logic execution, typically hidden from the user.
CLI (Command Line Interface): A text-based interface for interacting with a computer program through commands typed into a terminal or console.
Command Terminal: A text-based interface where users can input commands to perform various tasks on a computer system.
Desktop Application: Software designed to be run on desktop or laptop computers, providing functionality without requiring a web browser.
Entities: Objects or elements with distinct and independent existence within a system, often represented in databases or software architectures. MediCLI has 3 entities; Patient, Doctor, Appointment.
GUI (Graphical User Interface): An interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and visual indicators.
Hard Disk: A component of a computer system responsible for long-term storage of data.
Home Folder: The default directory or folder on a computer system where a user’s personal files and data are stored.
Java 11: A version of the Java programming language and platform, released in September 2018, known for its long-term support (LTS).
JavaFX: A software platform and GUI toolkit for Java applications, providing a rich set of features for building interactive user interfaces.
Jar File: A Java Archive file format used to package Java class files, associated metadata, and resources into a single file.
Json File: A file format used for storing and exchanging data in a human-readable and machine-parseable format, based on JavaScript Object Notation (JSON).
Logging Files: Files generated by software applications to record events, actions, or errors for troubleshooting and analysis purposes.
macOS: The operating system developed by Apple Inc. for its Macintosh line of computers.
NRIC (National Registration Identity Card): A unique identification document issued to citizens and permanent residents of certain countries.
Recursively Deleted: The process of removing entities from a filesystem in a recursive manner. (e.g If an Appointment ‘A’ was associated or ‘linked’ with Person ‘P’, the deletion of ‘P’ will also trigger the deletion of the Appointment ‘A’)
Ubuntu: A popular Linux distribution based on Debian, known for its ease of use and community-driven development.
Windows: A series of operating systems developed by Microsoft, widely used on personal computers and servers.
Command summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Add Patient |
addpatient i/NRIC n/NAME d/DOB p/PHONE_NUMBER e.g., addpatient i/S1234567A n/John Doe d/2003-01-30 p/98765432
|
| Add Doctor |
adddoctor i/NRIC n/NAME d/DOB p/PHONE_NUMBER e.g., adddoctor i/S1234567A n/John Doe d/2003-01-30 p/98765432
|
| Edit Person |
edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [i/NRIC] [d/DOB]e.g., edit 1 p/91234567 n/Betsy Crower
|
| Find Person |
find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., find Doe Li
|
| Query Patient |
patient KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., patient James Jake
|
| Query Doctor |
doctor KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., doctor John Doe
|
| Delete Person |
delete INDEXe.g., delete 3
|
| Add Appointment |
addappt ad/DATETIME dn/DOCTOR_NRIC pn/PATIENT_NRIC e.g., addappt ad/2024-08-11 23:50 dn/S1234567A pn/S1234567B
|
| Edit Appointment |
editappt INDEX ad/DATETIMEe.g., editappt 1 ad/2024-04-09 10:10
|
| Query Appointment by Patient |
apptforpatient KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., apptforpatient S1234567A
|
| Query Appointment by Doctor |
apptfordoctor KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., apptfordoctor S7654321A
|
| Delete Appointment |
deleteappt INDEXe.g., deleteappt 3
|
| Help | help |
| List | list |
| Clear | clear |
| Exit | exit |